Author: Aditya Kumar

Introduction to Vegan Leather
The fashion industry, once notorious for its environmental and ethical challenges, is undergoing a significant transformation with the vegan leather. Today, consumer preferences are shifting towards more sustainable and cruelty-free alternatives, driven by a growing awareness of the environmental and ethical implications of clothing production. One of the most prominent trends in this transformation is the rise of vegan fashion. This white paper explores the burgeoning demand for cruelty-free and sustainable alternatives, the vegan leather, to traditional animal-based materials in fashion, with a particular focus on vegan leather and plant-based textiles. It delves into the reasons behind this shift, the challenges faced by the industry, and the potential benefits for both consumers and the planet.
The Shift Towards Vegan Fashion:
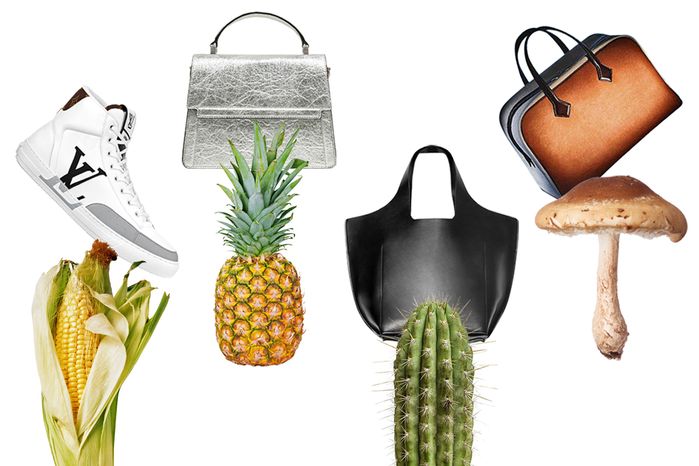
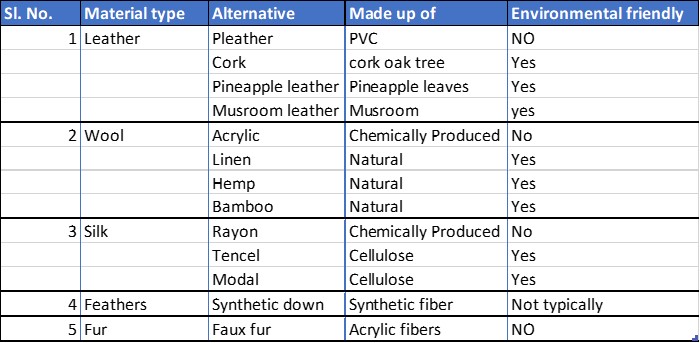

Leather Alternatives:
a. Pleather (PVC): While not entirely environmentally friendly due to its use of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), pleather serves as a synthetic leather substitute. It offers a cruelty-free alternative to traditional leather, which often involves animal suffering and environmental concerns.
b. Cork: Derived from the bark of cork oak trees, cork is an eco-friendly and recyclable material. Its use in fashion not only promotes sustainability but also helps in preserving cork oak forests, which play a vital role in carbon sequestration.
c. Pineapple Leather: Made from pineapple leaves, this material is not only cruelty-free but also environmentally friendly and recyclable. It has gained popularity for its sustainability and versatility.
d. Mushroom Leather: Mushroom-based leather, derived from mycelium, is another emerging alternative. It’s biodegradable and sustainable, making it an eco-conscious choice.
Wool Alternatives:
a. Acrylic: While acrylic is a chemically produced material, it provides an animal-free alternative to wool. However, its production can have environmental drawbacks, such as the release of microplastics during washing.
b. Linen: Linen, made from the flax plant, is a natural and biodegradable fiber. It is not only environmentally friendly but also offers a sustainable alternative to wool.
c. Hemp: Hemp, another natural fiber, is known for its durability and sustainability. Like linen, it provides a sustainable alternative to traditional wool.
d. Bamboo: Bamboo textiles are becoming increasingly popular for their softness and sustainability. They offer a cruelty-free alternative to wool.
Silk Alternatives:
a. Rayon: Although rayon is chemically produced, it serves as a silk alternative without the need for silkworms. However, the chemical processing can have environmental implications.
b. Tencel and Modal: These cellulose-based textiles are made from sustainably sourced wood pulp. They offer cruelty-free and eco-friendly alternatives to silk.
Feathers Alternative:
a. Synthetic Down: Synthetic down is cruelty-free and recyclable, providing a humane alternative to traditional feather-filled clothing items. It also reduces the demand for bird plumage, often obtained through unethical means.
Fur Alternative:
Faux Fur: Faux fur has gained popularity as a cruelty-free alternative to animal fur. It eliminates the need for fur farming, which is associated with significant ethical concerns.
Challenges and Benefits
The fashion industry’s transition towards vegan alternatives is not without its challenges. Manufacturers must grapple with finding innovative and sustainable materials that meet consumer expectations for quality and style. Additionally, production processes for some vegan materials can still have environmental impacts, albeit reduced when compared to their animal-based counterparts.
However, the benefits are compelling. Vegan fashion aligns with the growing demand for ethical and sustainable products. It helps reduce animal suffering, mitigates environmental harm, and promotes a circular economy through recyclable materials. Consumers can make more conscious choices, aligning their fashion preferences with their values and contributing to a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
The rise of vegan fashion represents a significant shift in the fashion industry, driven by changing consumer preferences and a heightened awareness of the environmental and ethical consequences of traditional clothing production. The adoption of cruelty-free and sustainable alternatives, such as vegan leather and plant-based textiles, showcases a commitment to a more humane and eco-conscious future. While challenges persist, the benefits for both consumers and the planet make this transition a vital step in reshaping the fashion industry for the better.
Read about cactus leather here, a transformative article on sustainable solution to leather.



Leave a Comment